Chapter 13: Thermochemistry
Section 13-1: Enthalpy of Reaction, ΔH
Section 13-2: Estimating ΔH Using Bond Energies
Section 13-3: Calculating ΔH Using Hess's Law
Section 13-4: Calculating ΔH° Using Standard Enthalpies of Formation, ΔHf°
Section 13-5: Heat Transfer and the First Law of Thermodynamic
Section 13-6: Experiment - Determining the Specific Heat of a Metal Using Calorimetry
Section 13-8: ΔH for Changes of Physical State and Heating/Cooling Curves
Section 13-9: Experiment - Determining ΔHfusion of Ice
Section 13-10: Lattice Energy and the Born-Haber Method
Chapter 13 Practice Exercises and Review Quizzes
Section 13-1: Enthalpy of Reaction, ΔH
Thermochemistry is
essentially the study of the heat released or absorbed by a reaction. A reaction that releases heat is said
to be exothermic, while a reaction
that absorbs heat is said to be endothermic. The heat released or absorbed by a
reaction under constant pressure conditions is known as the enthalpy of
reaction, ΔH. For an exothermic
reaction, ΔH will be negative, while ΔH will be positive for an endothermic
reaction. To express information
about the heat of a reaction, the value of ΔH is typically written after the
reaction in the unit kilojoules per mole as follows:
2 C2H6
(g) + 7 O2 (g) → 6 H2O(g) + 4 CO2 (g) ΔH = -3119 kJ/mol
Since ΔH is negative in this case,
we know that the reaction is exothermic and releases heat. We can use ΔH as a conversion factor in
the form
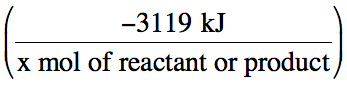
(where x
is the coefficient of the particular reactant or product being considered) to
convert between the actual amount reacted or produced and the actual amount of
heat released in a given reaction situation:
Sample Exercise 13A:
If 5.40 grams of ethane is burned
according to the combustion equation shown above, how much heat will be
released?
Solution:
Since we are considering the
reactant ethane, which has a coefficient of 2 in the equation above, x = 2 in
the conversion factor. We first
convert the grams of ethane to moles and then use the conversion factor to
convert to the amount of heat released:
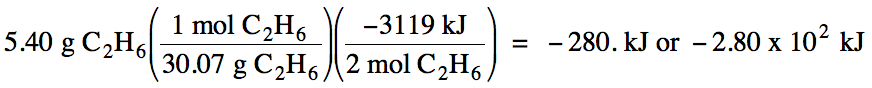
If instead we know the actual
amount of heat in kJ involved in a given reaction situation and we wish to
convert to the amount reacted or produced, we first use the conversion factor
with kJ in the denominator and mol in the numerator, and then we can convert
moles to any desired unit:
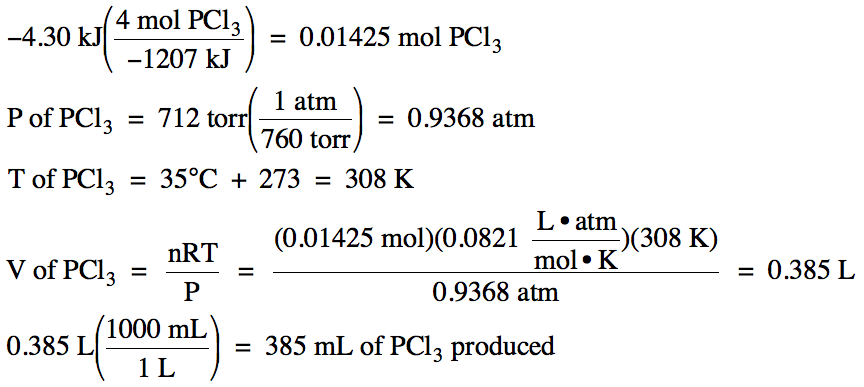
Sample Exercise 13B:
The formation of gaseous phosphorus
trichloride is shown below:
P4
(g) + 6 Cl2 (g) → 4 PCl3
(g)
ΔH = -1207 kJ/mol
If 4.30 kJ of heat are released as
the formation reaction above proceeds, how many milliliters of gaseous
phosphorus trichloride, measured at 35°C and 712 torr, will be produced?
Solution:
The question specifies that heat is released, so we will need to make the given amount of
heat negative and begin the calculation with -4.30 kJ. Since we are considering the product
phosphorus trichloride, which has a coefficient of 4 in
the equation above, x = 4 in the conversion factor. We first use the conversion factor to convert to moles of
phosphorus trichloride, then
we use the Ideal Gas Law to find the volume of phosphorus trichloride
produced:
Section 13-2: Estimating ΔH Using Bond Energies
The following table shows a variety
of different average bond energies:
|
Bond |
Average Bond Energy (kJ/mol) |
|
C-C |
347 |
|
C=C |
614 |
|
C≡C |
839 |
|
C-H |
414 |
|
C-O |
360 |
|
C=O |
745 |
|
F-F |
157 |
|
F-N |
272 |
|
N-N |
163 |
|
N=N |
418 |
|
N≡N |
941 |
|
O-H |
464 |
|
O-O |
142 |
|
O=O |
498 |
Breaking covalent bonds requires
energy to be absorbed and is endothermic, whereas forming covalent bonds
releases energy and is exothermic.
For a chemical reaction in which all the reactants and products are gases,
we can estimate ΔH by adding the positive energies absorbed to break all bonds
in the reactant molecules to the negative energies released by the formation of
all bonds in the product molecules, as demonstrated in the following problem:
Sample Exercise 13C:
Use average bond energies to
estimate ΔH for the following reaction:
2 NF3
(g) → N2
(g) + 3 F2 (g)
Solution:
First, draw a Lewis structure for
each reactant and product molecule:
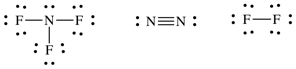
Then, being sure to take
coefficients into account, add the positive energies absorbed to break all
bonds in the reactant molecules to the negative energies released by the
formation of all bonds in the product molecules to find ΔH:
ΔH
(estimated) = (2x3)(N-F) – 1(N≡N) – 3(F-F)
= 6(272 kJ/mol) – 1(941 kJ/mol) – 3(157
kJ/mol) = 220 kJ/mol
Section 13-3: Calculating ΔH Using Hess's Law
When a reaction is reversed, the
sign of ΔH changes:
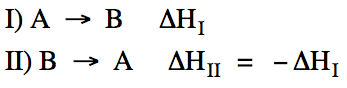
When all the
coefficients in a reaction are multiplied by the same number, ΔH is
multiplied by that same number as well:
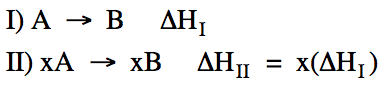
Hess's Law essentially states that the unknown ΔH for a reaction
of interest can be determined by adding together the ΔH values from a series of
two or more other reactions if the other reactions add up algebraically to the
reaction of interest. For example,
if we wish to find ΔH for the reaction A → C, we can
add together the ΔH values from the following two reactions:
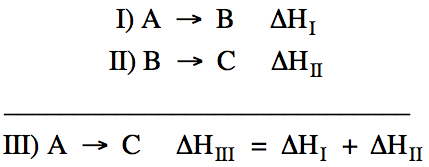
Reactions I and
II add up algebraically to reaction III because an equal amount of B
appears on both sides of the equation and, thus, can be canceled out.
In some cases, the given reactions
with known ΔH values may not add up to the reaction of interest with an unknown
ΔH. However, we may be able to
first reverse one or more of the given reactions (and, thus, switch the sign of
ΔH) and/or multiply all the coefficients of one or more of the given reactions
(and, thus, multiply ΔH by that same number) before adding the reactions to
find the unknown ΔH:
Sample Exercise 13D:
Calculate ΔH for the reaction C2H4
(g) + Cl2 (g) → C2H4Cl2
(l) using the following two reactions:
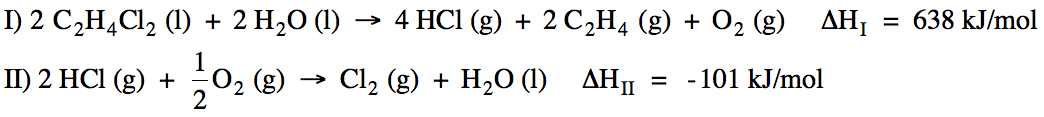
Solution:
Reactions I and
II do not add up algebraically to the reaction of interest. However, if we reverse Reaction I and
also multiply all the coefficients in Reaction I by ½ and then reverse
Reaction II, the new reactions will add up algebraically to the reaction of
interest because H2O (l), 2 HCl (g), and
½ O2 (g) will cancel out. Therefore, we can find the unknown ΔH by adding (-½ΔHI)
+ (-ΔHII):
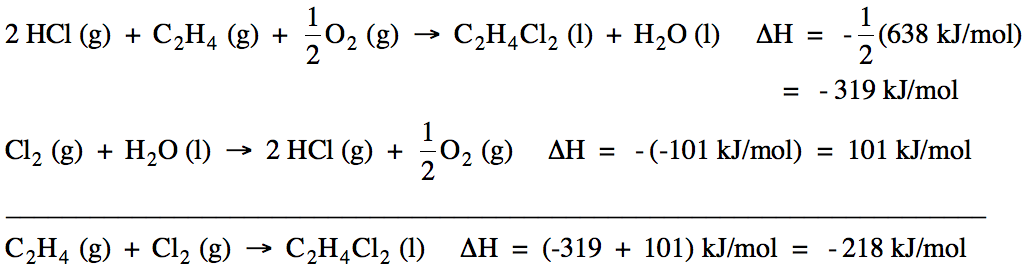
Section 13-4: Calculating ΔH° Using Standard
Enthalpies of Formation, ΔHf°
The following table categorizes all
elements into their standard states at 1 atm and
25°C, which is essentially room temperature:
|
Gases |
Liquids |
Solids |
|
Cl2,
F2, H2, N2, O2 + noble gases |
Br2,
Hg |
I2 + all other elements |
C(graphite)
is considered the standard state of solid carbon because it is more stable than
the other allotrope, C(diamond).
When a formation reaction is
written, 1 mole of a given compound is produced on the right side and each
element present in the compound is shown separately in its standard state as a
reactant on the left side:
Formation
Reaction: standard state elements → 1 mol compound
To balance the equation while
keeping 1 mole of the compound on the right side, it may be necessary to use
fractions on the left side. For
example, the formation reaction for solid ammonium iodide would be:
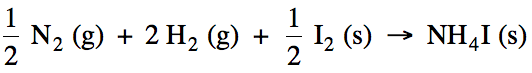
Sample Exercise 13E:
Write the balanced formation
reaction, including physical states, for solid sucrose, C12H22O11.
Solution:
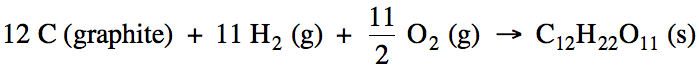
ΔH for a formation reaction is
known as the standard enthalpy of formation, ΔHf°,
and may be exothermic or endothermic.
However, ΔHf°
= 0 kJ/mol for all elements in their standard states.
ΔH for a reaction carried out at 1 atm is known as the standard enthalpy of reaction,
ΔH°. We can determine ΔH° for a
reaction using known ΔHf° values and
Hess's Law. For example, consider
the reaction aA + bB → cC + dD, where a and b are the
coefficients of the reactants A and B, and c and d are the coefficients of the
products C and D. Hess's Law
suggests that we can determine ΔH° for this reaction by adding the following
steps:

We can generalize this approach as
follows:
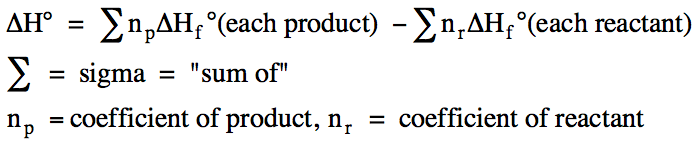
Sample Exercise 13F:
Calculate ΔH° for the reaction 2 H2S
(g) + 3 O2 (g) → 2 H2O
(l) + 2 SO2 (g) using the following information:
|
Compound |
ΔHf° (kJ/mol) |
|
H2S
(g) |
-20.6 |
|
H2O
(l) |
-285.8 |
|
SO2
(g) |
-296.8 |
Solution:
ΔHf° = 0 kJ/mol for the standard state element O2
(g), so ΔH° = [2(-285.8) + 2(-296.8) - 2(-20.6) - 3(0)] kJ/mol = -1124.0 kJ/mol
Section 13-5: Heat Transfer and the First Law of
Thermodynamics
Calorimetry is
essentially the measurement of heat in the laboratory. To calculate the quantity of heat (q)
in joules gained (positive value) when a substance increases in temperature or
lost (negative value) when a substance decreases in temperature, without a
change in physical state, we multiply the mass (m) of the substance in grams by
the specific heat (s) of the substance in J/g•°C and
also by the temperature change of the substance (tfinal
– t initial) in °C:
q = msΔt = ms(tf – ti)
Sample Exercise 13G:
The specific heat of copper metal
is 0.385 J/g•°C. How much heat in joules and in kilojoules is lost when a 165
gram sample of copper metal is cooled from 98°C to 26°C?
Solution:
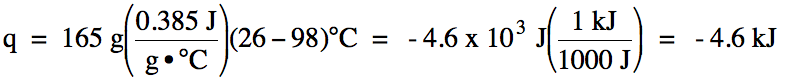
The First Law of Thermodynamics has been referred to as the Law of
Conservation of Energy and essentially states that energy can neither be
created nor destroyed. In calorimetry experiments, if one substance at a higher
temperature is placed together with a second substance at a lower temperature
in an insulated container that does not allow heat entry or exit, both
substances will eventually reach the same final temperature. Furthermore, the First Law of
Thermodynamics suggests that the amount of heat lost by the higher temperature
substance will be exactly equal to the amount of heat gained by the lower
temperature substance:
qlost = -qgained
Note that, although the magnitude of
heat will be equal, qlost is
exothermic and will have a negative sign, whereas qgained
is endothermic and will have a positive sign.
Section 13-6: Experiment - Determining the Specific
Heat of a Metal Using Calorimetry
The specific heat of water is known
to be 4.18 J/g•°C. If a metal with unknown specific heat but known mass and
initial temperature is mixed in an insulated calorimeter, such as a securely-covered Styrofoam coffee cup, with a known mass of
water that also has a known initial temperature, the specific heat of the metal
can be determined as follows:
Sample Exercise 13H:
In an insulated calorimeter, a 175
gram piece of aluminum metal originally at 304°C was added to 925 grams of
water originally at 22°C. The
final temperature of the aluminum-water mixture was 33°C. Determine the specific heat of
aluminum.
Solution:
According to the First Law of
Thermodynamics, the amount heat lost by the aluminum metal will be exactly
equal to the amount of heat gained by the water (but opposite in sign):
qAl lost = -qwater gained
We first calculate the amount of
heat the water gained and then switch the sign to find the amount of heat the
aluminum lost, after which we can calculate the specific heat of aluminum:
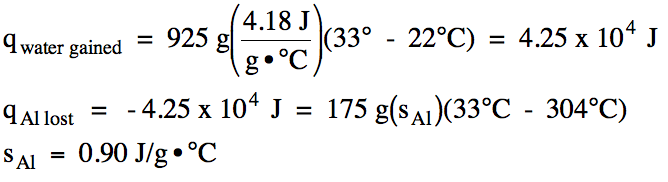
If we know the masses, specific heats, and initial temperatures of both the metal and the water, we can calculate the final temperature in the calorimeter after mixing, as demonstrated below in Practice Exercise 13-9.
Section 13-7: Experiment – Determining ΔH Using
Calorimetry
When a solid ionic compound (salt)
is dissolved in water, the cations and anions become
separated from each other and are hydrated as water molecules surround the ions
to create ion-dipole interactions. If this process is exothermic, the reaction
particles will release heat into the surrounding mixed solution and increase
the temperature of the solution.
If this process is endothermic, the reaction particles will absorb heat
from the surrounding mixed solution and decrease the temperature of the
solution. We can determine the
heat lost or gained by the reaction, qrxn,
by first calculating the heat lost or gained by the surrounding solution, qsoln, and then switching the sign:
qrxn = -qsoln
After finding qrxn
and converting to kilojoules, we can divide by the moles of salt dissolved to
find ΔH for the process in kJ/mol of salt dissolved:
Sample Exercise 13I:
In an insulated calorimeter, 2.6 grams of solid ammonium chloride at 23.4°C was dissolved in 35.9 grams of water also at 23.4°C, after which the final temperature of the mixed solution was 18.6°C. If the specific heat of the mixed solution was 3.94 J/g•°C, determine ΔH for the dissolving process NH4Cl (s) → NH4Cl (aq) in kJ/mol NH4Cl.
Solution:
Since the temperature of the mixed
solution decreased, the mixed solution lost heat and the reaction particles
gained heat in an endothermic reaction with ΔH > 0:
qrxn gained = -qsoln lost
We first calculate the amount of
heat the mixed solution lost and then switch the sign to find the amount of
heat the reaction particles gained, after which we can convert to kilojoules
and divide by the moles of ammonium chloride to find ΔH for the dissolving
process NH4Cl (s) → NH4Cl
(aq):
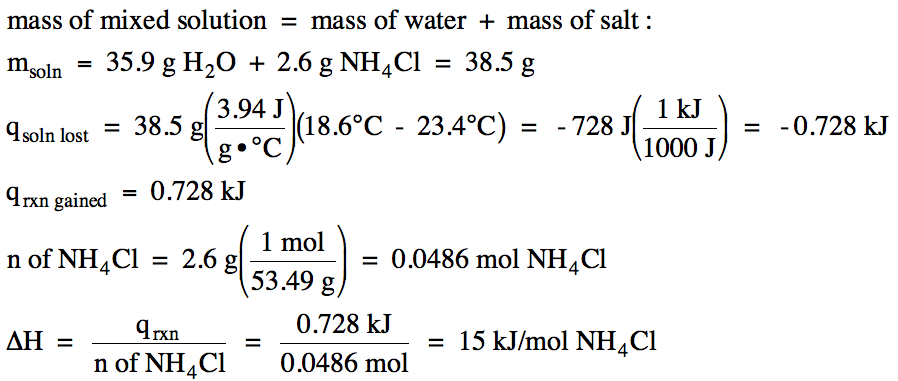
For neutralization reactions
between an aqueous acid and an aqueous metal hydroxide, the process of
determining ΔH by calorimetry is similar to that used
for the dissolving of ionic salts, but the calculation typically differs in the
following two ways:
1. Instead of masses being given,
we may be given the volume of each solution being mixed, which we then can add
to obtain the total volume of the mixed solution that absorbs heat from or
releases heat into the reaction particles. If we are given the density of the mixed solutions, we can
multiply by the volume of the mixed solutions to obtain the mass of the mixed
solutions that is necessary in the calculation of qsoln.
2. In the final step, we divide qrxn by the moles of a specified product formed in
the reaction from the limiting reagent to obtain ΔH for the reaction.
Sample Exercise 13J:
In an insulated calorimeter, 45 mL of 1.0 M hydrochloric acid was mixed with 42 mL of 1.0 M sodium hydroxide, with both solutions
originally at 19.4°C. The final
temperature of the mixed solutions was 25.9°C. The density of the mixed solutions was 1.03 g/mL and the specific heat of the mixed solutions was 4.02 J/g•°C. Write a
balanced molecular equation, including physical states, and determine ΔH for
the neutralization reaction in kJ/mol of water formed.
Solution:
HCl (aq) + NaOH
(aq) → H2O
(l) + NaCl (aq)
Since the temperature of the mixed
solutions increased, the mixed solutions gained heat and the reaction particles
lost heat in an exothermic reaction with ΔH < 0:

Section 13-8: ΔH for Changes of Physical State and
Heating/Cooling Curves
Changes of physical state occur at
a constant temperature. The
endothermic change from solid to liquid is known as fusion and occurs at the
melting point of the substance. To
calculate the amount of heat absorbed when a given amount of a substance is
melted, we multiply the moles melted by ΔH for the fusion process:
q = (nmelted)(ΔHfusion)
If the same amount of the substance
was frozen from a liquid to a solid rather than melted, the magnitude of heat
involved would be exactly the same, but heat would be released in the
exothermic process and q would be negative:
q = (nfrozen)(-ΔHfusion)
The endothermic change from liquid
to gas is known as vaporization and occurs at the boiling point of the
substance. To calculate the amount
of heat absorbed when a given amount of a substance is vaporized, we multiply
the moles vaporized by ΔH for the vaporization process:
q = (nvaporized)(ΔHvaporization)
If the same amount of the substance
was condensed from a gas to a liquid rather than vaporized, the magnitude of
heat involved would be exactly the same, but heat would be released in the
exothermic process and q would be negative:
q = (ncondensed)(-ΔHvaporization)
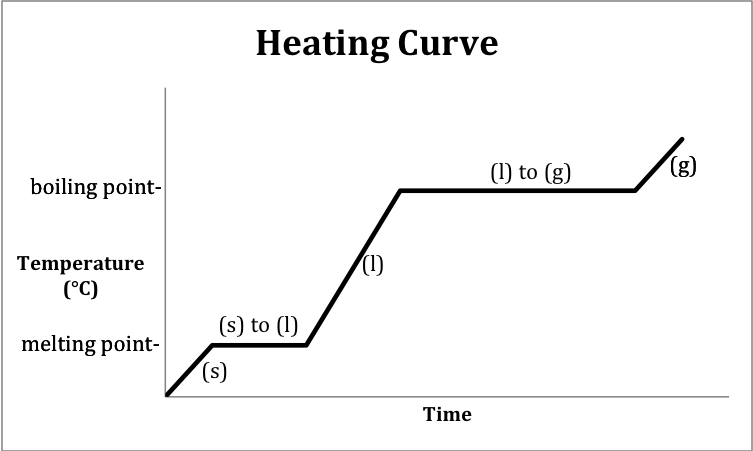
A heating curve is a graph that
depicts the changes in temperature and physical state that occur over time as
heat is absorbed by a substance.
The following sketch represents the general format of a heating curve
for a substance originally below the melting point in the solid state being
heated until it is a gas above the boiling point:
A cooling curve is a graph that
depicts the changes in temperature and physical state that occur over time as
heat is released by a substance.
The following sketch represents the general format of a cooling curve
for a substance originally above the boiling point in the gas state being
cooled until it is a solid below the melting point (same temperature as
freezing point):
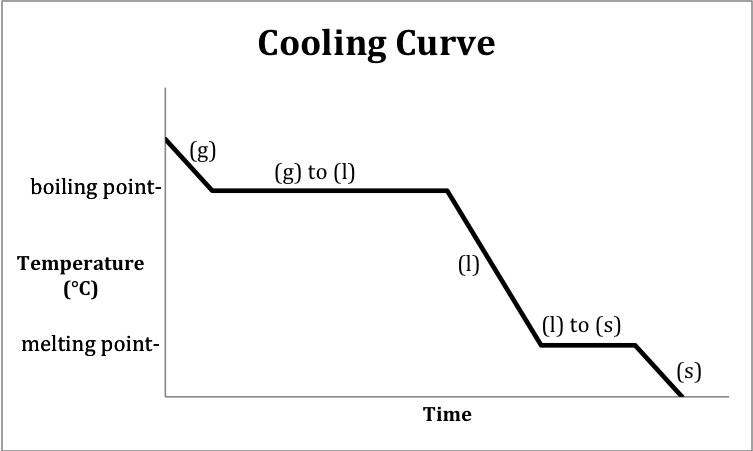
Note that heating and cooling
curves may encompass a less narrow temperature range and, therefore, may not
include all five of the distinct segments shown in the two sketches above.
Sample Exercise 13K:
Consider the following data for H2O:
Melting
Point = 0.0°C
Boiling
Point = 100.0°C
ΔHfusion = 6.01 kJ/mol
ΔHvaporization = 40.8 kJ/mol
Specific
Heat of Ice = 2.03 J/g•°C
Specific
Heat of Water = 4.18 J/g•°C
Specific
Heat of Water Vapor = 1.99 J/g•°C
Sketch a heating curve that depicts
ice at -25.0°C being heated until the temperature reaches 125.0°C and then
calculate the total amount of heat in kilojoules absorbed when 175 grams of H2O
undergoes this process.
Solution:
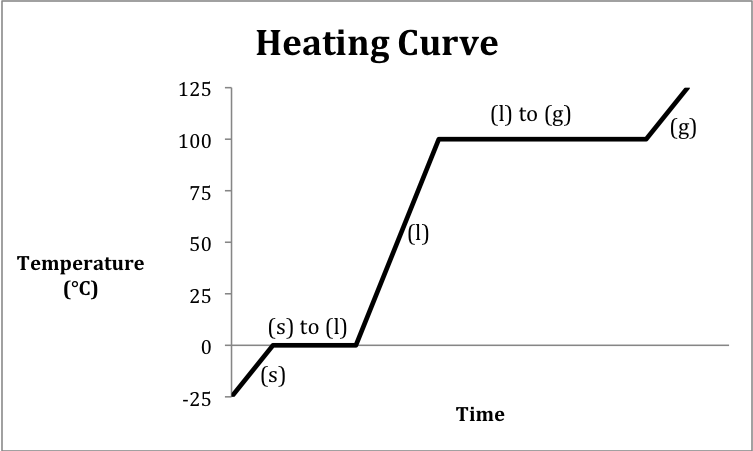
We first calculate the amount of
heat absorbed along each of the five distinct segments of the heating curve and
then add the five heat values together to find the total heat absorbed:
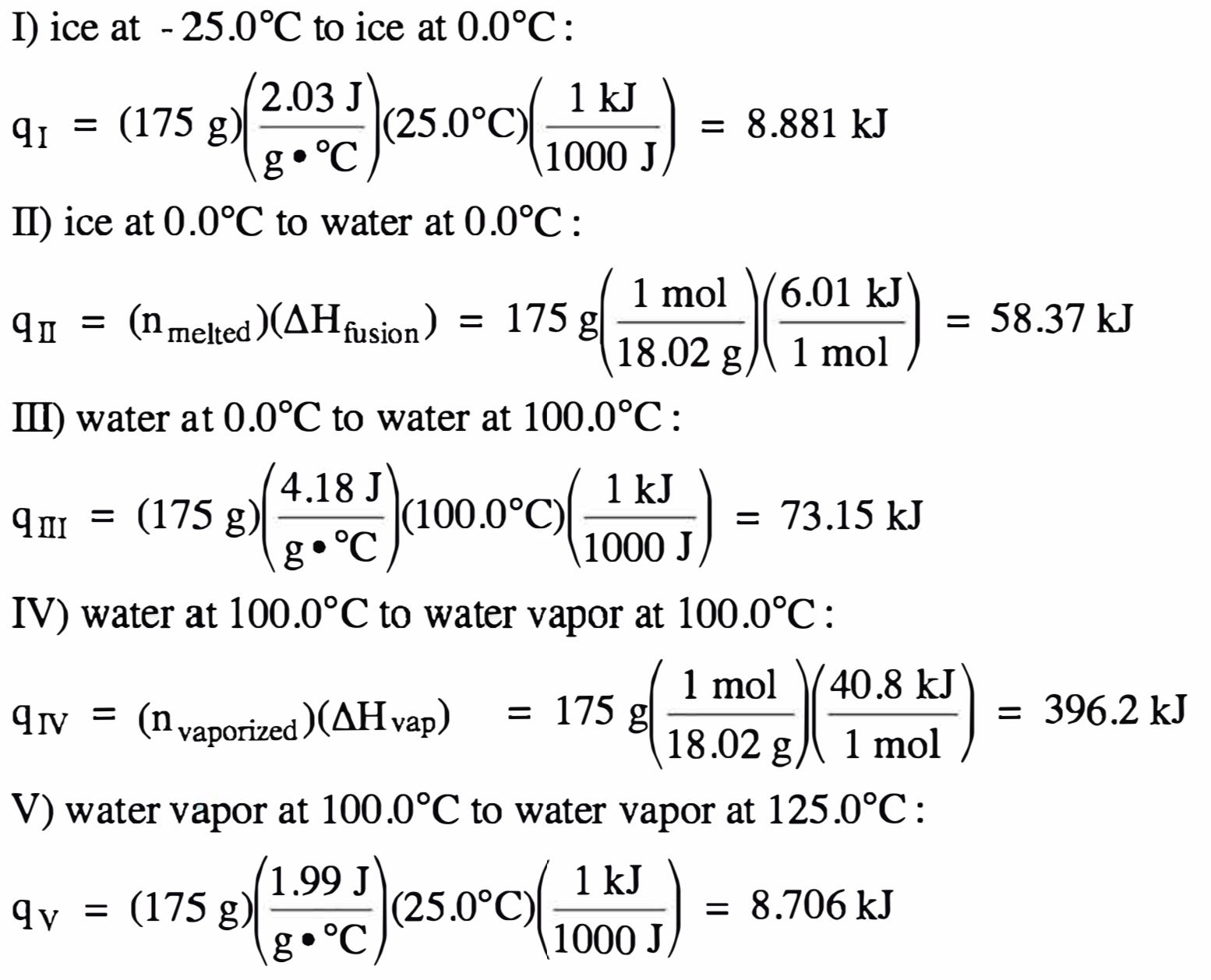
qtotal = 8.881 kJ
+ 58.37 kJ + 73.15 kJ + 396.2 kJ + 8.706 kJ = 545 kJ
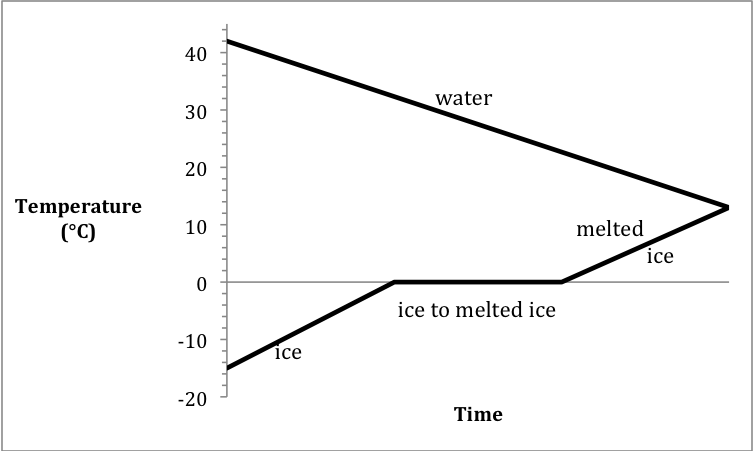
Section 13-9: Experiment – Determining ΔHfusion of Ice
Given the specific heats of ice and
water in the previous problem, we can determine ΔHfusion
of ice in the laboratory by mixing in an insulated calorimeter a known mass of
ice at a known original temperature below 0°C with a known mass of water at a
known original temperature above 0°C.
If we use enough water and/or a high enough original water temperature,
all the ice will melt and the final temperature in the calorimeter will be
above 0°C. The sketch below
depicts the heating curve for the ice as its temperature rises to its melting
point, the ice melts, and then the temperature of the melted ice rises to the
final temperature. On the same
sketch, the cooling curve for the water as it cools from its original
temperature to the final temperature is also included:
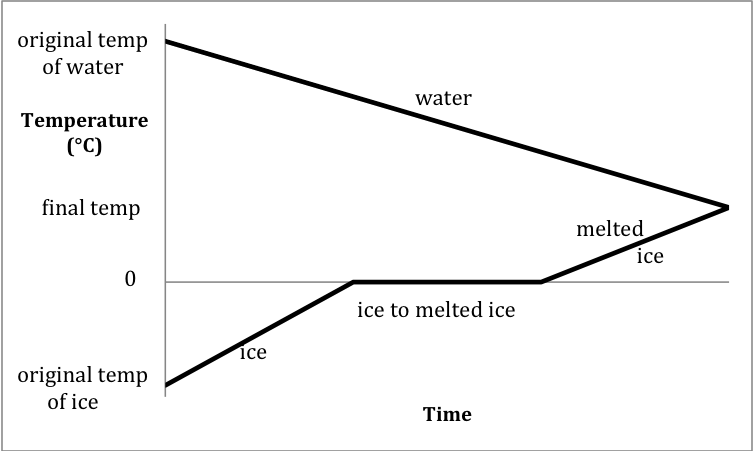
The heat lost by the water as it
cools to the final temperature will be equal in magnitude but opposite in sign
to the total heat gained by the ice in the three segments of the heating curve
above, which will allow us to determine ΔHfusion
of ice:
Sample Exercise 13L:
In an experiment to determine ΔHfusion of ice, a student added 29.04 grams of
ice originally at -15.1°C to 97.91 grams of water originally at 41.9°C in an
insulated calorimeter. If the
final temperature in the calorimeter was 13.2°C, calculate the experimentally
determined ΔHfusion of ice.
Solution:
The heating curve for the ice +
cooling curve for the water is:
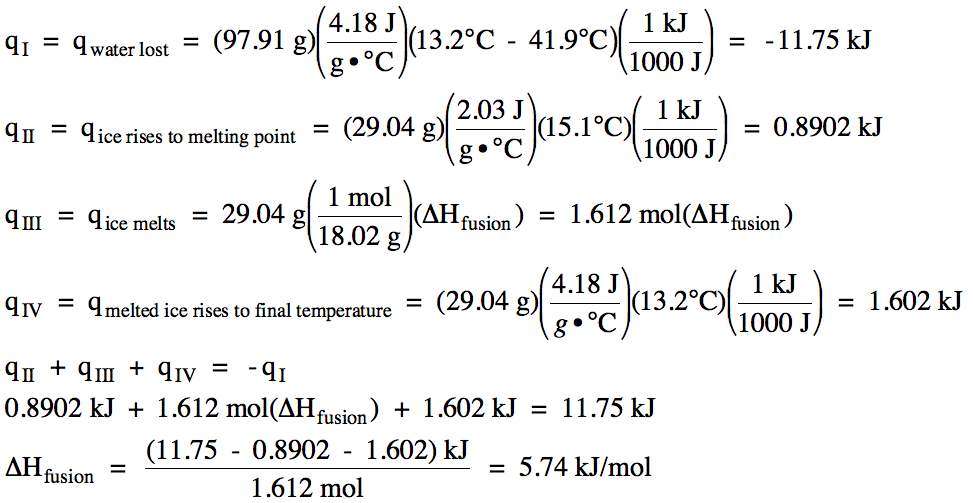
Section 13-10: Lattice Energy and the Born-Haber
Method
1 mol
ionic (s) → metal
cations (g) + nonmetal anions (g) ΔH =
L.E.
Lattice energy generally is higher when the magnitudes of the ionic charges are larger
and the sizes of the ions are smaller due to increased Coulombic attraction. The Born-Haber method utilizes Hess’s Law to calculate lattice energy by
adding a combination of reactions from the following table:
Reaction Type
|
ΔH
|
X (s) → X (g)
|
ΔHsublimation
|
X (l) → X (g)
|
ΔHvaporization
|
X2 (g) → 2 X (g)
|
X2 bond energy
|
X (g) → X+ (g) + e-
|
first
ionization energy = I1
|
X (g) → X2+ (g) + 2 e-
|
first +
second ionization energy = I1 + I2
|
X (g) + e- → X- (g)
|
first
electron affinity = EA1
|
X (g) + 2
e-→ X2- (g)
|
first +
second electron affinity = EA1 + EA2
|
1 mol
ionic (s) → metal
cations (g) + nonmetal anions (g)
|
lattice
energy = L.E.
|
standard
state metal + nonmetal → 1 mol
ionic (s)
|
ΔHf°
for ionic (s)
|
Reactions from the table above are
added as follows:
1a) convert
standard state metal to gas
1b) convert
standard state nonmetal to gas (if necessary)
2) break
bond in gaseous diatomic nonmetal to form neutral gaseous nonmetal atoms
3) remove
electrons from neutral gaseous metal atoms to form gaseous metal cations
4) add
electrons to neutral gaseous nonmetal atoms to form gaseous nonmetal anions
5) combine
gaseous metal cations and nonmetal anions to form 1 mol solid ionic compound
____________________________________________________________________________
6) combine
standard state metal and nonmetal to form 1 mol solid ionic compound
If we are given ΔH for all
reactions above except reaction 5, we can use Hess’s Law to solve for ΔH of
reaction 5, which is equal in magnitude but opposite in sign to the lattice energy of the ionic compound:
Sample Exercise 13M:
Calculate the lattice energy of
sodium chloride using the information below. Show all relevant reactions, including states of matter.
ΔHsublimation of sodium = 107 kJ/mol
Cl2 bond energy = 244 kJ/mol
first
ionization energy of sodium = 496 kJ/mol
first
electron affinity of chlorine = -349 kJ/mol
ΔHf°
of solid sodium chloride = -411 kJ/mol
Solution:
1a) Na (s) → Na (g) ΔHsublimation = 107 kJ/mol
2) 1/2 Cl2 (g) → Cl (g) 1/2(Cl2 bond energy) =1/2(244 kJ/mol)
3) Na (g) → Na+ (g) + e- I1 = 496
kJ/mol
4) Cl (g) +
e-→ Cl- (g) EA1 = -349 kJ/mol
5) Na+ (g) + Cl- (g) → NaCl
(s) - L.E.
______________________________________________________________
6) Na (s) +
1/2 Cl2 (g) → NaCl
(s) ΔHf° = -411 kJ/mol
107 kJ/mol
+ 1/2(244 kJ/mol) + 496 kJ/mol + (-349 kJ/mol) + (- L.E.) = -411 kJ/mol
L.E. of
NaCl = 787 kJ/mol
If we are given the lattice energy but not ΔHf°, we can use the Born-Haber method to calculate ΔHf°, as demonstrated below in Practice Exercise 13-18.
Chapter 13 Practice Exercises and Review Quizzes:
13-1) The
decomposition of ammonia gas into nitrogen gas and hydrogen gas is endothermic:
2 NH3
(g) → N2
(g) + 3 H2 (g) ΔH = 92 kJ/mol
If 762 mL
of hydrogen gas, measured at 325°C and 792 mmHg, is formed in the reaction
above, how much heat will be absorbed?
Click for Solution
13-1)
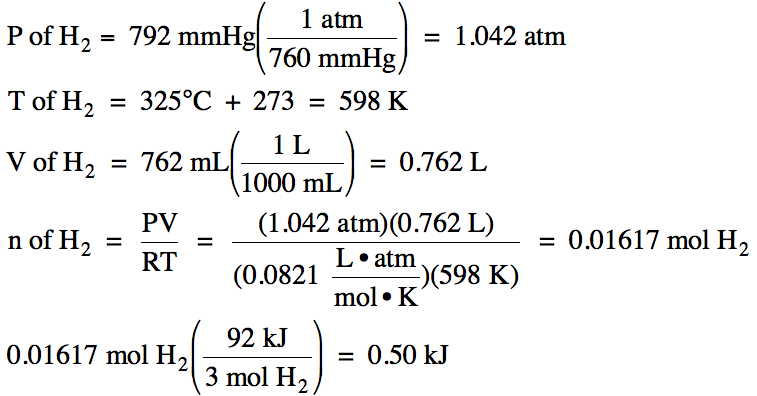
13-2) Consider
the following reaction:
2 ZnS (s) + 3 O2 (g) → 2 ZnO
(s) + 2 SO2 (g) ΔH = -878 kJ/mol
What mass of solid ZnS, in kilograms, must react according to the equation
above in order for 5.41 x 103 kJ of heat to be released?
Click for Solution
13-2) Heat is released = must start
with -5.41 x 103 kJ:
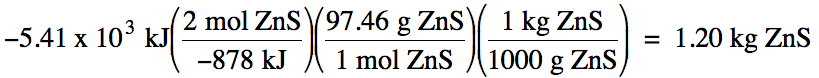
13-3) For the reaction 2 CH3OH (g) + 3 O2 (g) → 2 CO2 (g) + 4 H2O (g), estimate ΔH using average bond energies.
Click for Solution
13-3) 2 CH3OH (g) + 3 O2
(g) → 2 CO2
(g) + 4 H2O (g)
Lewis
structures:
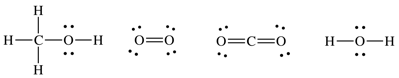
ΔH
(estimated) = (2x3)(C-H) + (2x1)(C-O) + (2x1)(O-H) + (3x1)(O=O)
-
(2x2)(C=O) - (4x2)(O-H)
= 6(414
kJ/mol) + 2(360 kJ/mol) + 2(464 kJ/mol) + 3(498 kJ/mol)
- 4(745
kJ/mol) – 8(464 kJ/mol) = -1066 kJ/mol
13-4) Calculate ΔH for the reaction
4 NH3 (g) + 5 O2 (g) → 4 NO (g) +
6 H2O (l) using the following three reactions:
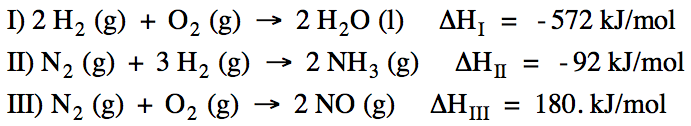
Click for Solution
13-4) Reactions I + II + III do not
add up algebraically to the reaction of interest. However, if we multiply all the coefficients in Reaction I
by 3, if we reverse Reaction II and multiply all coefficients in Reaction II by
2, and if we multiply all the coefficients in Reaction III by 2, the new
reactions will add up algebraically to the reaction of interest because 2 N2
(g) and 6 H2 (g) will cancel out. Therefore, we can find the unknown ΔH by adding (3ΔHI)
+ (-2ΔHII) + (2ΔHIII):
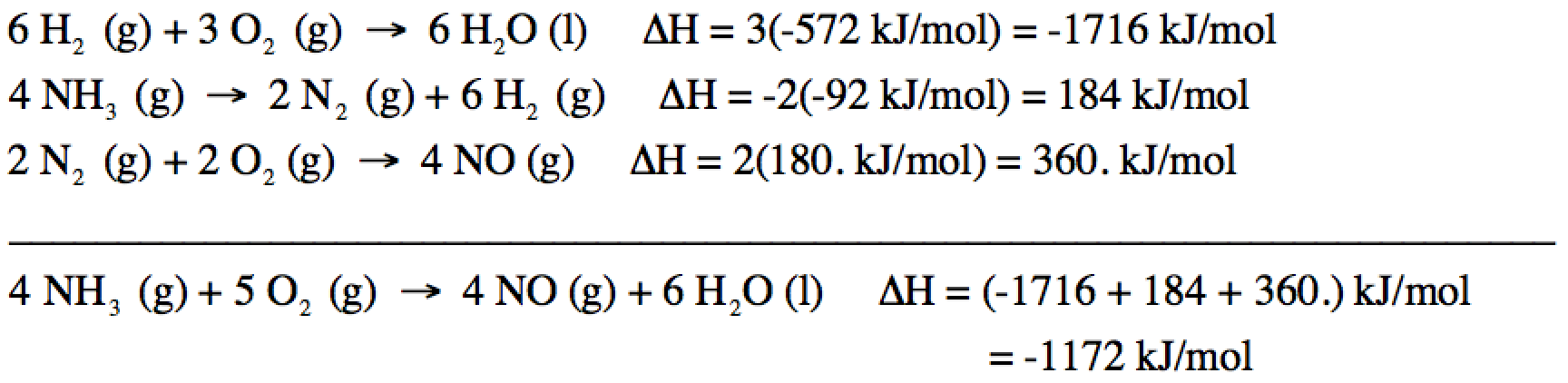
13-5) Write
the balanced formation reaction, including physical states, for liquid tribromomethane, CHBr3.
Click for Solution
13-5)
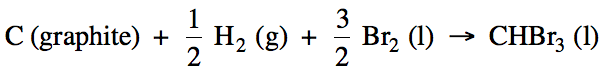
13-6) Calculate ΔH° for the
reaction 2 C4H10 (g) + 13 O2 (g) → 10 H2O(g)
+ 8 CO2 (g) using the following information:
|
Compound |
ΔHf° (kJ/mol) |
|
C4H10
(g) |
-126.5 |
|
H2O
(g) |
-241.8 |
|
CO2
(g) |
-393.5 |
Click for Solution
13-6) ΔH° = [10(-241.8) + 8(-393.5)
- 2(-126.5) - 13(0)] kJ/mol
13-7) The
specific heat of lead metal is 0.130 J/g•°C. How much heat in joules and in
kilojoules is gained when a 225 gram sample of lead metal is heated from 125°C
to 241°C?
Click for Solution
13-7)
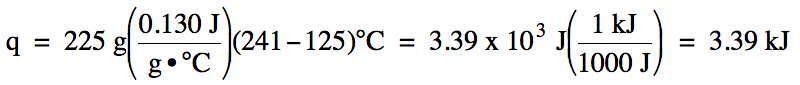
13-8) In
an insulated calorimeter, a 225 gram piece of iron metal originally at 463°C
was added to 845 grams of water originally at 27°C. The final temperature of the iron-water mixture was 39°C. Determine the specific heat of iron.
Click for Solution
13-8)
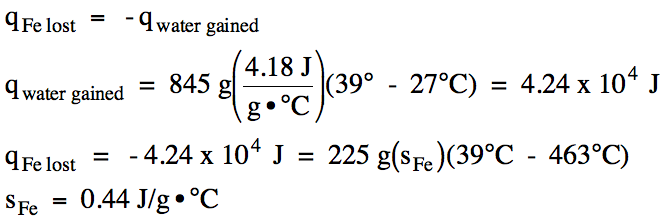
13-9) The specific heat of titanium metal is 0.54 J/g•°C. In an insulated calorimeter, a 265 gram piece of titanium metal originally at 285°C was added to 645 grams of water originally at 26°C. Determine the final temperature of the titanium-water mixture.
Click for Solution
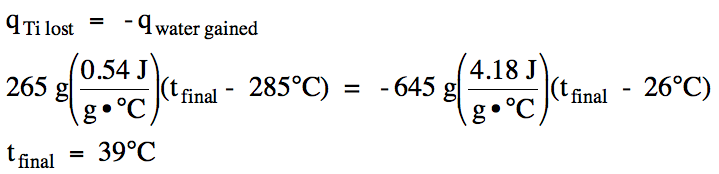
13-10) In
an insulated calorimeter, 12.7 grams of solid calcium chloride at 21.4°C was
dissolved in 129.1 grams of water also at 21.4°C, after which the final
temperature of the mixed solution was 38.3°C. If the specific heat of the mixed solution was 3.89 J/g•°C, determine ΔH for the dissolving process CaCl2
(s) → CaCl2
(aq) in kJ/mol CaCl2.
Click for Solution
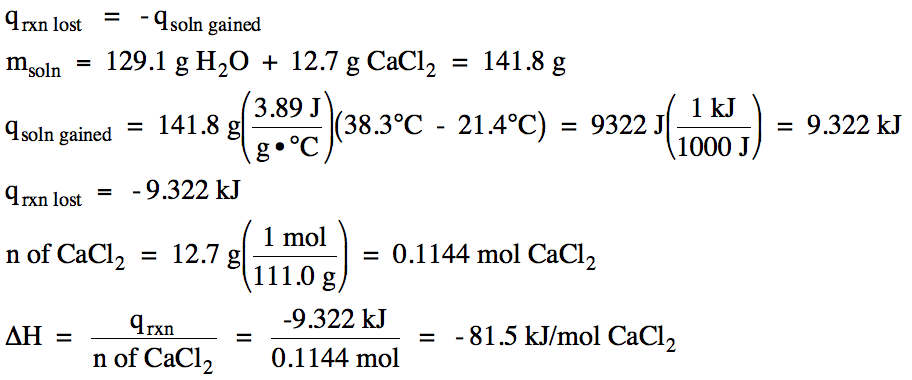
13-11) In an insulated calorimeter,
85.6 mL of 2.55 M nitric acid was mixed with 94.3 mL of 2.51 M potassium hydroxide, with both solutions
originally at 22.6°C. The final
temperature of the mixed solutions was 39.1°C. The density of the mixed solutions was 1.04 g/mL and the specific heat of the mixed solutions was 3.98 J/g•°C. Write a
balanced molecular equation, including physical states, and determine ΔH for
the neutralization reaction in kJ/mol of water formed.
Click for Solution
13-11) HNO3 (aq) + KOH (aq) → H2O (l) + KNO3
(aq)
Since the temperature of the mixed
solutions increased, the mixed solutions gained heat and the reaction particles
lost heat in an exothermic reaction with ΔH < 0:

13-12) Consider
the following data for ethanol, C2H5OH:
Melting
Point = -114°C
Boiling
Point = 78°C
ΔHfusion = 5.0 kJ/mol
ΔHvaporization = 42.6 kJ/mol
Specific
Heat of Liquid Ethanol = 2.5 J/g•°C
Sketch a cooling curve that depicts
ethanol vapor at 78°C being cooled until solid ethanol is formed at -114°C and
then calculate the total amount of heat in kilojoules released when 55 grams of
ethanol undergoes this process.
Click for Solution
13-12) In this case, there are only
three distinct segments on the cooling curve because the ethanol vapor is
already at the boiling point to start and the solid ethanol formed does not
cool below the melting/freezing point:
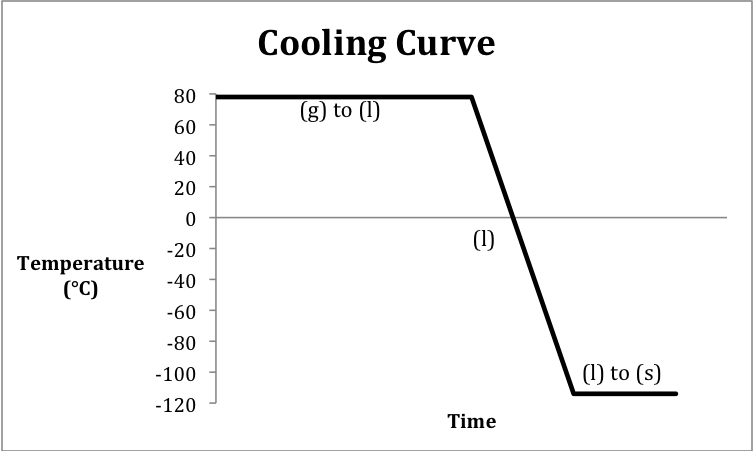
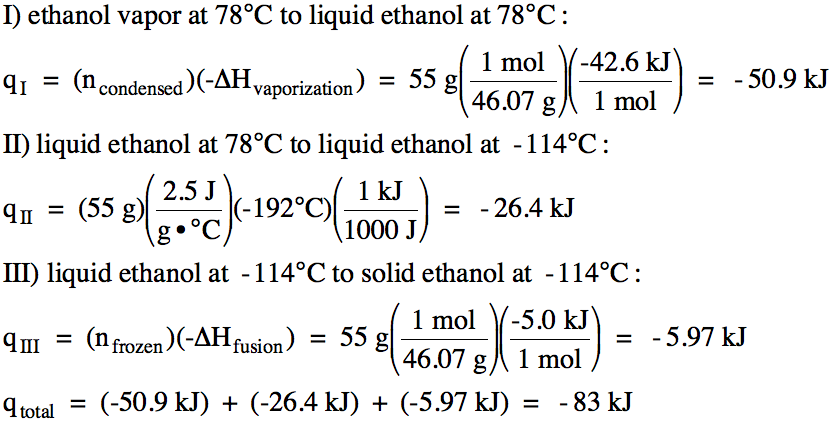
We first calculate the amount of
heat released along each of the three distinct segments of the cooling curve
and then add the three heat values together to find the total heat released:
13-13) Given the reaction 2 F2 (g) + O2 (g) → 2 OF2 (g) ΔH = 50. kJ/mol, use the
table of average bond energies to calculate the F-O bond energy.
Click for Solution
Lewis
structures:
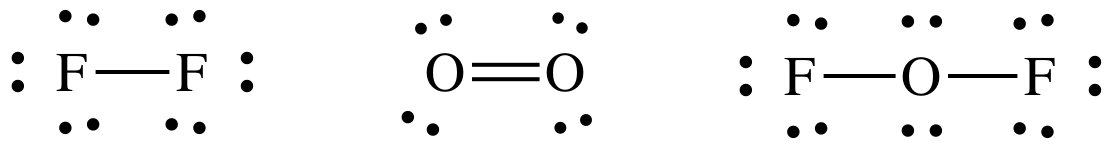
ΔH = 2(F-F)
+ 1(O=O) – (2x2)(F-O)
50. kJ/mol
= 2(157 kJ/mol) + 1(498 kJ/mol) – 4(F-O)
bond energy of F-O = 191 kJ/mol
13-14) Given the reaction N2H4 (l) + 2 H2O2 (l) → N2 (g) + 4 H2O (g) ΔH° = -643 kJ/mol, use the information below to calculate the standard
enthalpy of formation, ΔHf°, for H2O2 (l):
Compound
|
ΔHf° (kJ/mol)
|
H2O
(g)
|
-242
|
N2H4 (l)
|
51
|
Click for Solution
ΔH° = -643
kJ/mol = 1(0 kJ/mol) + 4(-242 kJ/mol) – 1(51 kJ/mol) – 2(ΔHf°
for H2O2 (l))
ΔHf°
for H2O2 (l) = -188 kJ/mol
13-15) ΔH for the dissolving process KOH (s) → KOH (aq) is -57.6 kJ/mol KOH. In an insulated calorimeter, 18.7 grams of solid potassium hydroxide at 21.3°C was dissolved in 115.5 grams of water also at 21.3°C. If the specific heat of the mixed solution was 3.88 J/g•°C, determine the final temperature in the calorimeter.
Click for Solution
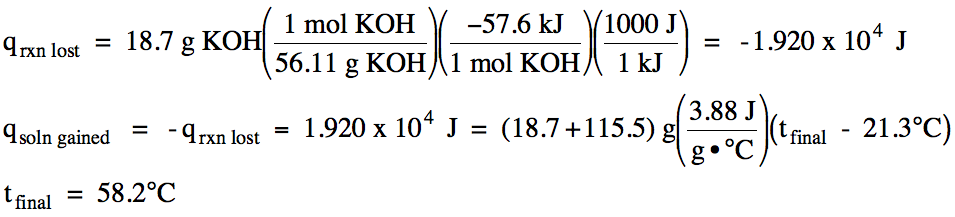
13-16) Consider the reaction Ca(OH)2 (aq) + 2 HCH3COO (aq) → 2 H2O (l) + Ca(CH3COO)2 (aq) ΔH = -108 kJ/mol. In an insulated calorimeter, 93.6 mL of 1.09 M calcium hydroxide at 19.6°C was mixed with 84.8 mL of 1.78 M acetic acid also at 19.6°C. If the density of the mixed solution was 1.03 g/mL and the specific heat of the mixed solution was 3.94 J/g•°C, determine the final temperature in the calorimeter.
Click for Solution
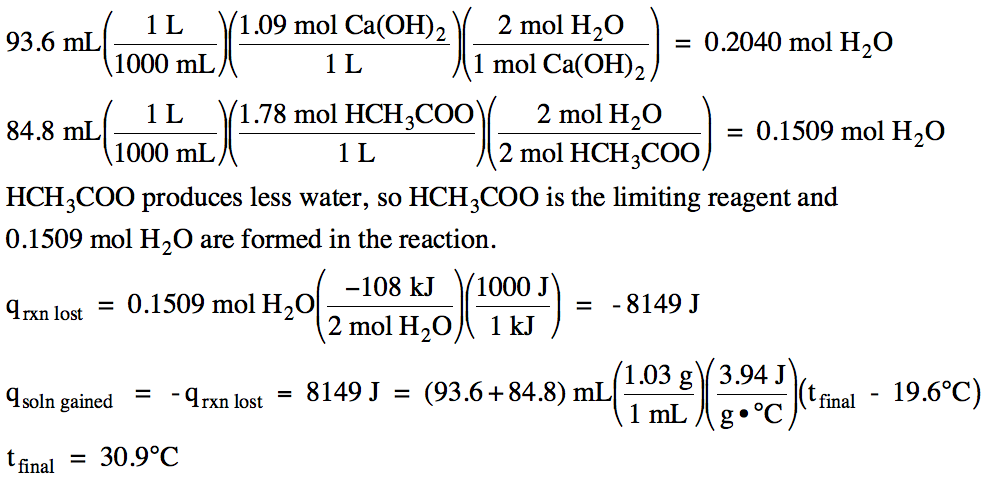
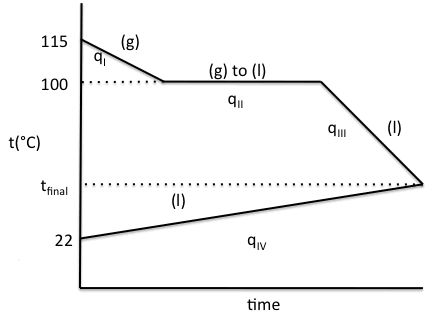
13-17) If 5.5 grams of water vapor
at 115°C is injected into an insulated calorimeter containing 175 grams of
water at 22°C, and all the water vapor condenses, sketch a heating/cooling curve for the process and determine the final
temperature of the liquid water in the calorimeter.
Click for Solution
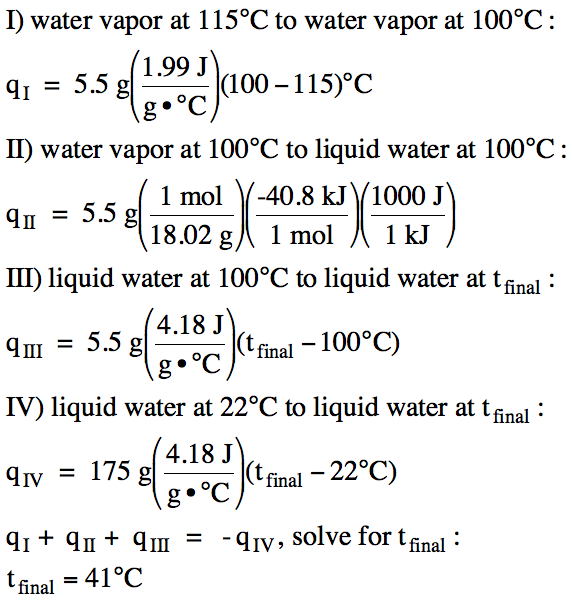
13-18) Calculate ΔHf° of
solid calcium oxide using the information below. Show all relevant reactions, including states of matter.
ΔHsublimation of calcium = 178 kJ/mol
O2 bond energy = 499 kJ/mol
first
ionization energy of calcium = 589 kJ/mol
second
ionization energy of calcium = 1145 kJ/mol
first
electron affinity of oxygen = -141 kJ/mol
second
electron affinity of oxygen = 744 kJ/mol
lattice energy of calcium oxide = 3401 kJ/mol
Click for Solution
1a) Ca (s) → Ca (g) ΔHsublimation = 178 kJ/mol
2) 1/2 O2 (g) → O (g) 1/2(O2 bond energy) =1/2(499 kJ/mol)
3) Ca (g) → Ca2+ (g) + 2 e- I1 + I2 = (589 + 1145) kJ/mol
4) O (g) + 2
e-→ O2- (g) EA1 + EA2 = (-141 + 744) kJ/mol
5) Ca2+ (g) + O2- (g) → CaO
(s) - L.E. = -3401
kJ/mol
______________________________________________________________
6) Ca (s) +
1/2 O2 (g) → CaO
(s) ΔHf° = ?
178 kJ/mol
+ 1/2(499 kJ/mol) + (589 + 1145) kJ/mol + (-141 + 744) kJ/mol + (-3401 kJ/mol)
= -637 kJ/mol = ΔHf° of CaO (s)
Click for Review Quiz 1 Answers
